Traffic Expert Witness
Traffic signals are the silent controllers of urban and suburban roadways, orchestrating traffic movement, improving safety, and reducing congestion. From simple red-yellow-green lights to advanced AI-based systems, the world of traffic signals is far more complex than it appears.
In this guide, we’ll explore all types of traffic signals, including the basics covered by industry blogs like Greenlight Traffic Engineering, and expand with advanced, specialized, and often-overlooked systems that are shaping modern mobility.


satisfied clients
These are pre-programmed signals that operate on a set schedule, regardless of actual traffic flow. They’re suitable for areas with predictable traffic patterns.
These systems use real-time data from traffic cameras, sensors, and other smart devices to adjust signal timings on the go.
These are not typically covered in basic blogs but are crucial in modern traffic engineering.
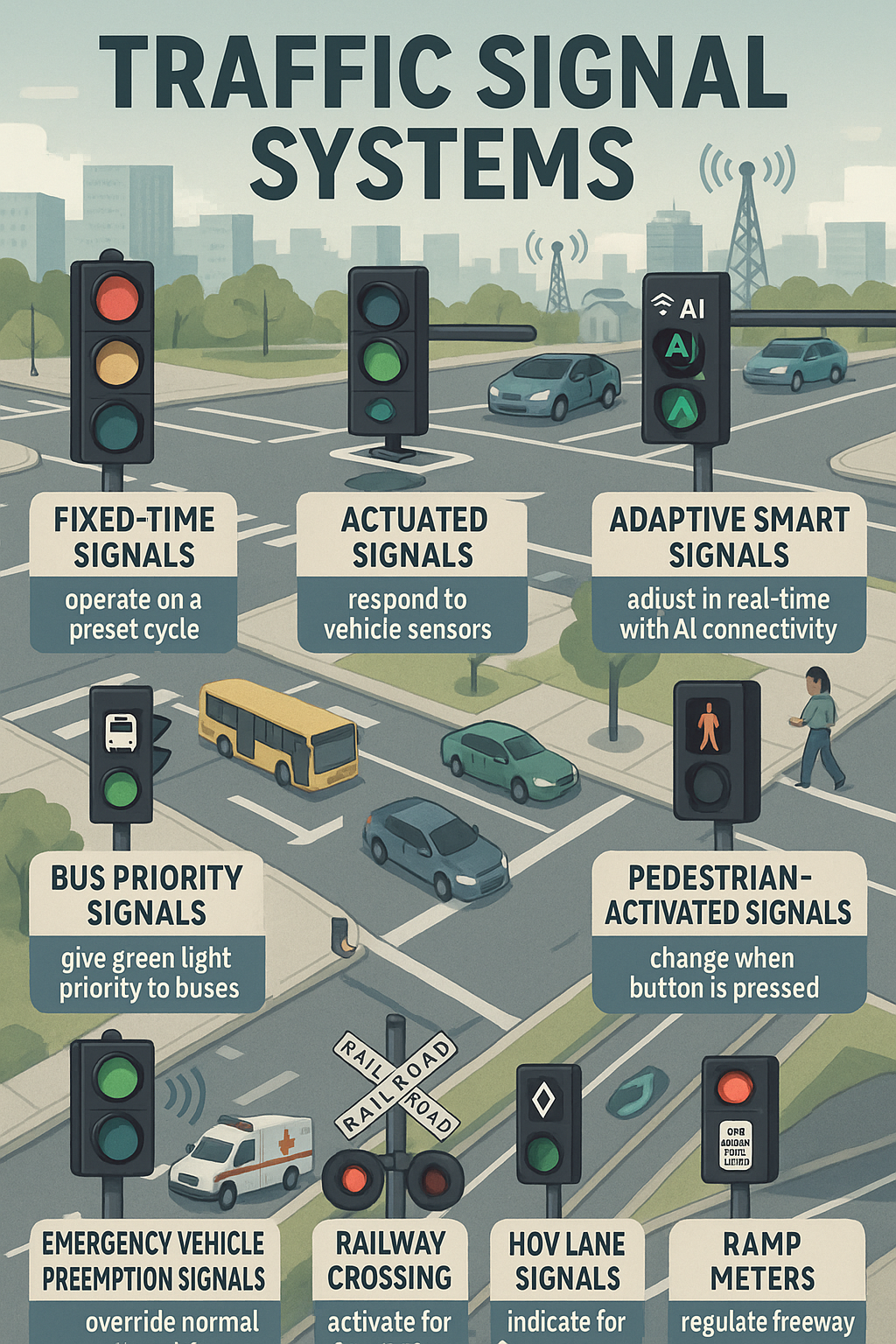
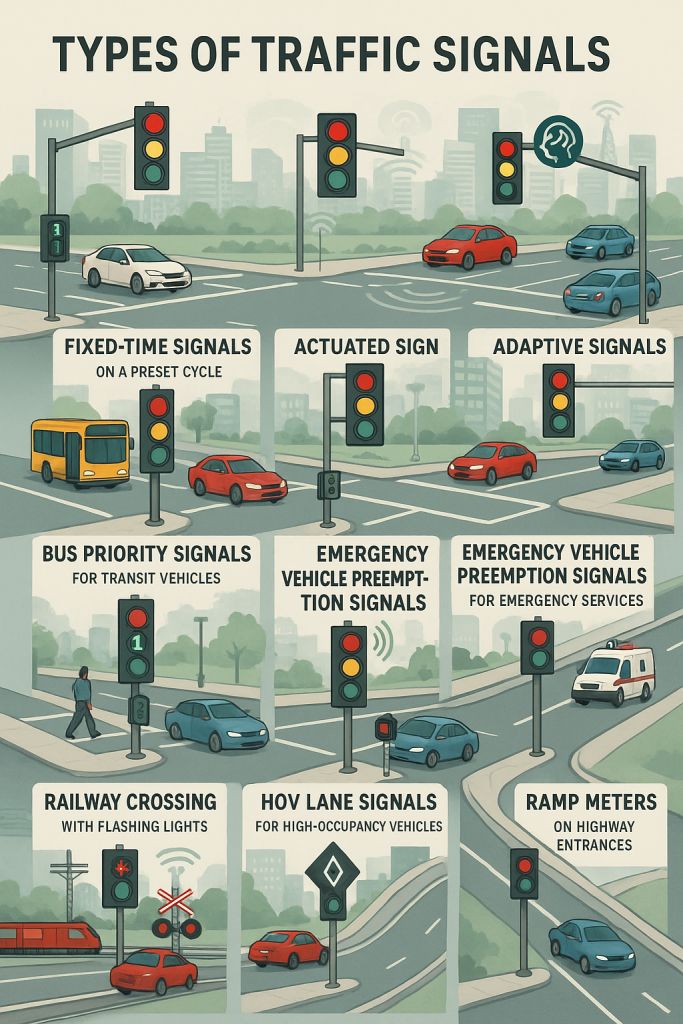
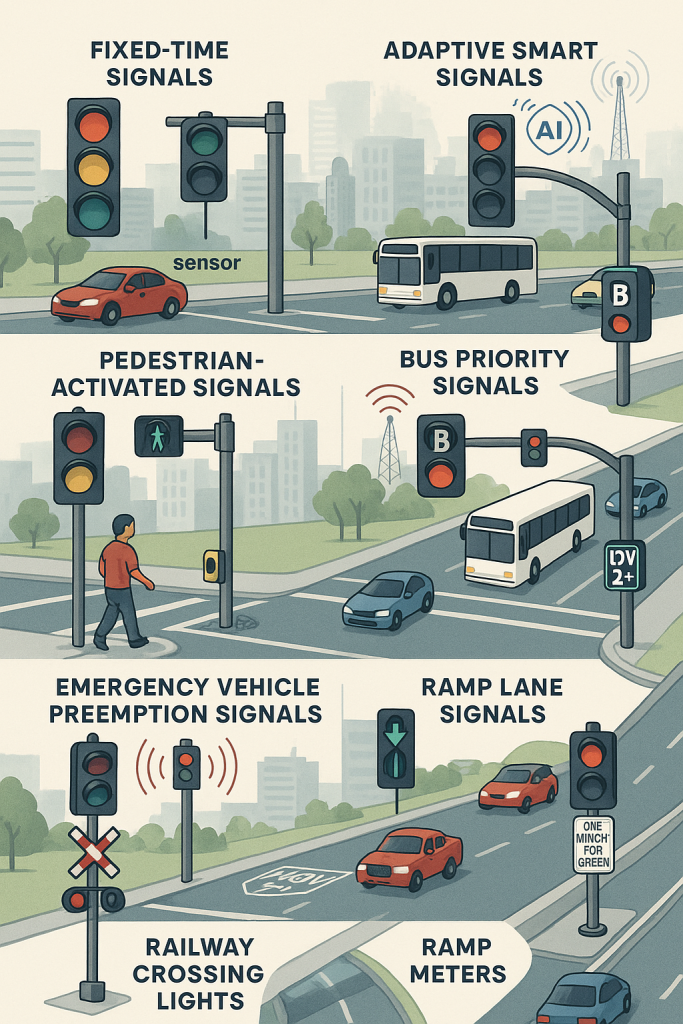
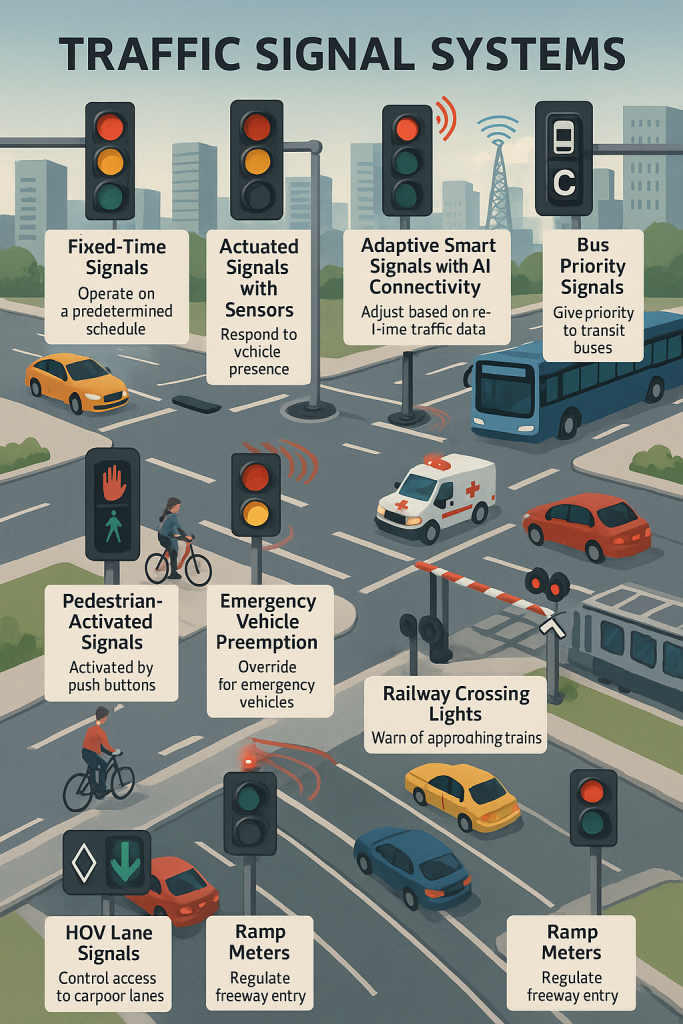
Located near intersections, these metal boxes house the electronics and control logic that operate the traffic signal.




Traffic signals are the backbone of urban mobility from simple time-based lights to ultra-modern smart signals that talk to vehicles. By understanding not only the types but also the technology, planning, and future trends, cities and engineers can build safer and more efficient transportation systems.

I provide attorneys and insurance adjusters in Mesa, AZ with the technical expertise they need in cases involving traffic accidents, roadway design, and traffic control.